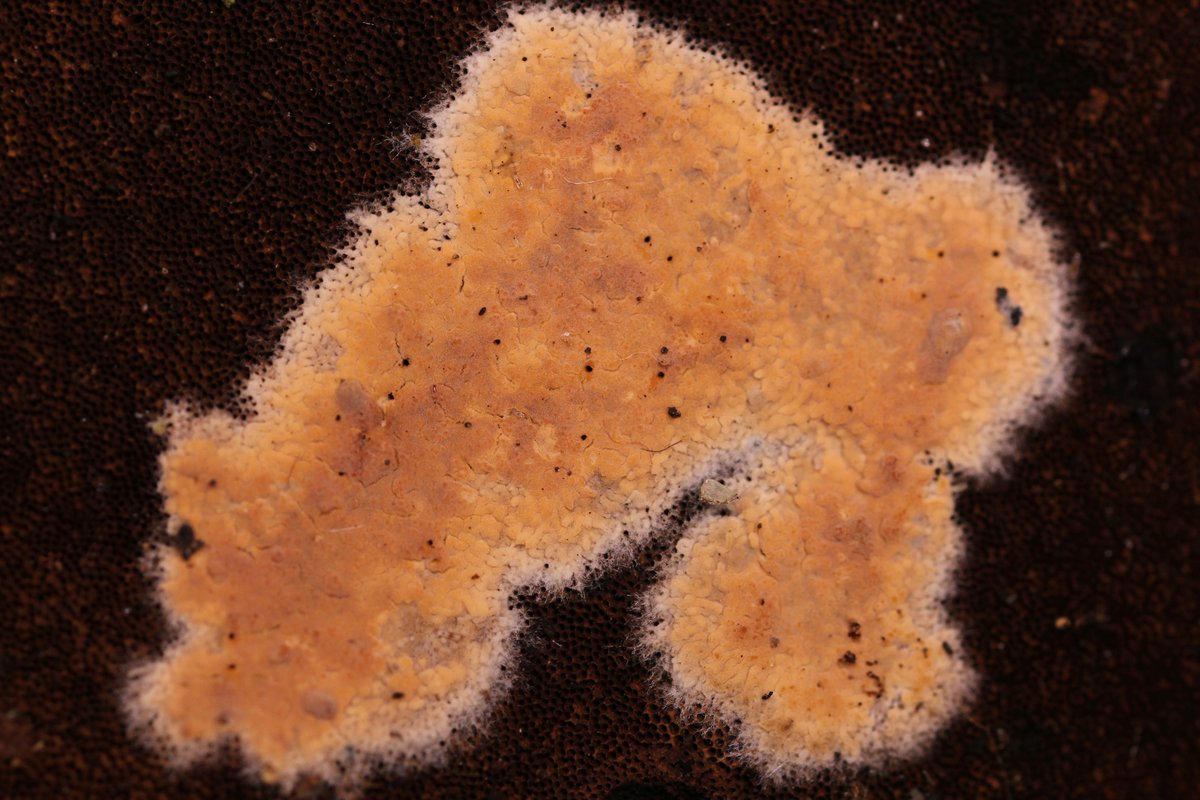
Mycobernardia incrustans (Parmasto) Ghob.-Nejh.
Previously known as Galzinia incrustans, Mycobernardia incrustans is a "true" corticioid fungus, belonging to the eponymous crust family, Corticiaceae (Ghobad-Nejhad et al. 2021). In Scandinavia, researchers found that prescribed burns are important for maintaining wood-rotting fungal species diversity, including populations of Mycobernardia incrustans, which are prevalent on charred wood a few years after a fire event (Olsson and Jonsson 2010). The specimen studied here was found growing on another fungus — a conk. It is unclear whether the crust was using the polypore as a perch to better disperse its spores or if it was digesting the polypore for nutrition.
A genome sequence for this species is available through JGI MycoCosm.
Details
White-rot saprotroph on decayed wood, reported as preferring wet habitats (Eriksson and Ryvarden 1975).
Effused, fragile, ceraceous when fresh, pruinoise when dry; hymenial surface even to grandinoid, cream-colored; margin indeterminate.
Not determined.
Not determined.
Not determined.
Rarely recorded, known from Eastern North America and Europe. View all sequenced specimens on iNaturalist.
Microscopy
Hyphal system: Monomitic, hyphae with clamps, thin-walled, hyaline, (1.8) 2.6–4.2 (4.3) µm wide (n = 10). Basidia: Terminal (although occassional presence of repetitive basidia reported in the literature), cylindrical to utriform, length (14.5) 17.2–29.5 (33) µm, width (3.4) 3.7–4.5 (4.6) µm, x̄ = 23.3 ✕ 4.1 µm, with four sterigmata and a basal clamp (n = 10). Basidiospores: Smooth, thin-walled, hyaline, inamyloid, curved, narrowly cylindrical (cylindrical to allantoid), length (4.9) 5.2–6.0 (6.3) µm, width (1.5) 1.8–2.2 (2.4) µm, x̄ = 5.6 ✕ 2.0 µm, Q (2.3) 2.5–3.1 (4.1), usually with one guttule, but sometimes none or two or more guttules (n = 30). Sterile structures: Absent.
Studied Specimens
BHI-F0664 (iNat172318325). 21 March 2017. Grape Island, Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area, Suffolk Co., MA, USA, 42.2693 -70.9218. Farlow Fungarium. Sequences: MF289562 (ITS).
References
-
Bernicchia A, Gorjón SP. 2010. Corticiaceae s.l. Italia: Candusso. 1008 p. Link
-
Eriksson J, Ryvarden L. 1975. The Corticiaceae of North Europe Volume 3: Coronicium — Hyphoderma. Oslo, Norway: Fungiflora. Link
-
Ghobad-Nejhad M, Langer E, Nakasone K, Diederich P, Nilsson RH, Rajchenberg M, Ginns J. 2021. Digging up the roots: taxonomic and phylogenetic disentanglements in Corticiaceae s.s. (Corticiales, Basidiomycota) and evolution of nutritional modes. Frontiers in Microbiology 12. PDF Link
-
Olsson J, Jonsson BG. 2010. Restoration fire and wood-inhabiting fungi in a Swedish Pinus sylvestris forest. Forest Ecology and Management 259:1971–1980. PDF Link
Citation
Dirks, Alden. 2026. Species profile for Mycobernardia incrustans (Parmasto) Ghob.-Nejh. CrustFungi.Com. https://crustfungi.com/species/mycobernardia-incrustans/. Accessed 2026-02-21.